 Posted By kawaib user
Posted By kawaib user- Comments 0
Everything you need to know about receding gums: a comprehensive guide
Oral health is an essential part of a person’s overall health, and gums play a vital role in maintaining dental stability and overall oral health, as receding gums is a common condition that can affect many people, whether they realize it or not, as gum recession is characterized by receding gum tissue around the teeth, exposing the roots of the teeth and making them more susceptible to tooth decay and sensitivity and this condition is an indicator of deeper oral health problems, and may lead to serious complications if not treated properly and in this article, we will discuss the different causes of receding gums, how to recognize their symptoms, and the options available for treatment and prevention to maintain the health of your gums and your beautiful smile.
What is the phenomenon of receding gums?
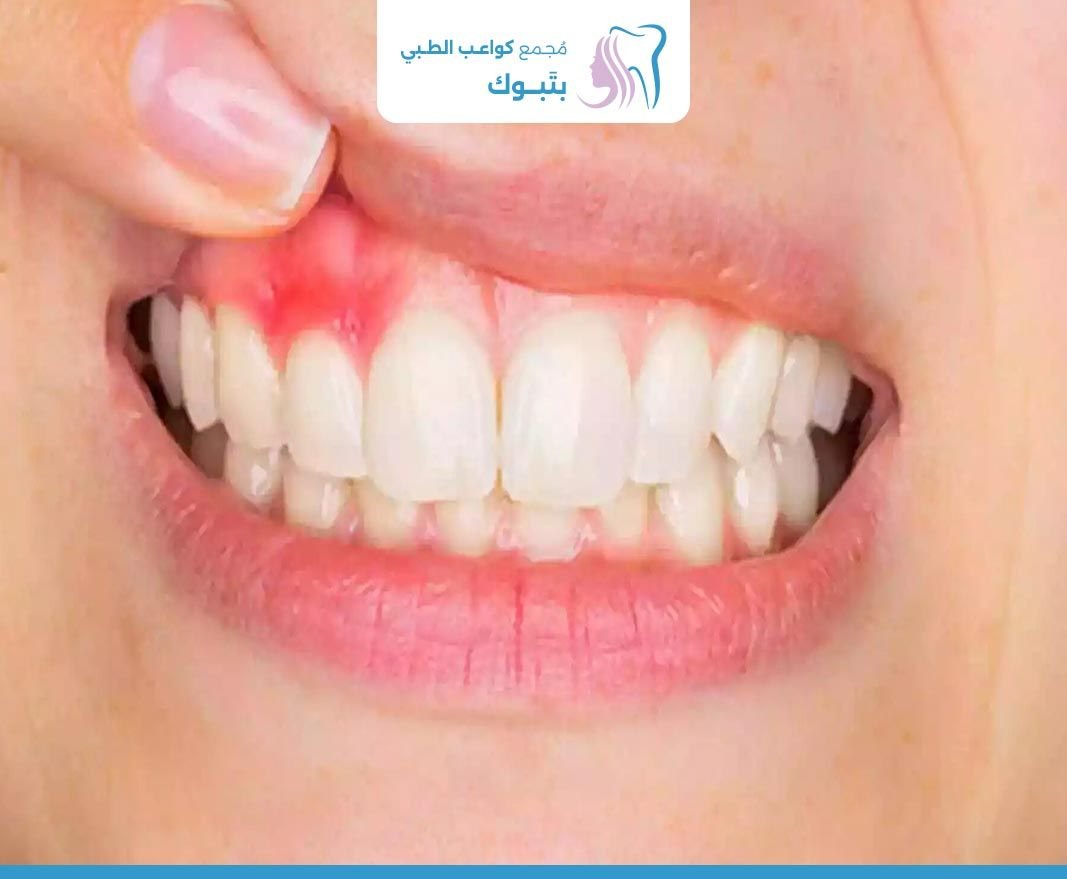
Gum recession is a condition in which the gum tissue surrounding the teeth recedes, exposing part of the tooth roots and this condition can be caused by several factors, making teeth more susceptible to cavities, allergies, and other health problems.
What are the causes of the phenomenon of receding gums?
There are many causes for the phenomenon of receding gums, and they include health, behavioral and genetic factors and below are the most prominent reasons that may lead to receding gums:
Gum disease (gingivitis and periodontitis):
Gingivitis: occurs as a result of the accumulation of plaque and bacteria on the teeth, leading to irritation and inflammation of the gingival tissue.
Periodontitis: A more advanced condition than gingivitis that damages the bone and tissue that support the teeth, causing the gums to recede.
Violent brush:
Using a hard toothbrush or brushing too vigorously can lead to gum tissue erosion and recession.
Poor oral care:
Not brushing your teeth properly and regularly contributes to the accumulation of plaque and tartar, which leads to gum irritation and recession.
Genetic factors:
Genetic factors can be a reason for an increased susceptibility to gum recession, as a person can inherit thin gums or weak gum tissue.
Hormonal changes:
Hormonal changes during periods such as puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to receding.
Smoking:
Smoking is a major factor that negatively affects gum health, as it reduces blood flow to the gums and increases plaque buildup.
Unbalanced teeth:
Crowded or misaligned teeth may cause uneven pressure on the gums, causing them to recede.
Teeth grinding (bruxism):
The pressure caused by teeth grinding, whether while awake or asleep, can cause gum erosion and recession.
Orthotics:
Using orthodontic appliances incorrectly or for long periods of time can lead to gum irritation and receding.
Lip or tongue piercing:
Lip or tongue piercings can cause constant friction with the gums, causing them to become irritated and recede.
What are the symptoms of receding gums?
Symptoms of receding gums are many, and include visual and sensory signs that can indicate receding gum tissue. The following are the most prominent symptoms that may indicate receding gums:
Tooth sensitivity:
Increased sensitivity to cold or hot drinks, as well as sweet or sour foods, due to exposure of tooth roots.
Appearance of tooth roots:
Notice the decline of the gum line and the appearance of part of the tooth roots that are usually covered by gums.
Bleeding gums:
Bleeding gums while brushing teeth or using dental floss.
Redness and swelling of gums:
Inflammation and swelling of the gums surrounding the teeth, which may be red and painful to the touch.
Bad breath:
Persistent bad breath, which may result from the accumulation of bacteria and plaque in the affected areas.
Change in the appearance of teeth:
Teeth appear longer than usual due to receding gum line.
Gum pockets:
It forms deep pockets between the gums and teeth, where plaque and tartar can accumulate, increasing the risk of gingivitis.
Teeth loosening:\
In advanced cases, loosening of the teeth may occur due to the loss of supporting tissue and surrounding bone.
Change in occlusion:
Feeling a change in the way the teeth align when biting or chewing.
What are the methods of treating receding gums?
Treatments for receding gums vary depending on how advanced the condition is and the underlying causes. Treatments include non-surgical and surgical interventions, as well as modifications in oral care, as the following are the most prominent methods of treating receding gums:
Non-surgical treatments
Good oral care:
Brush your teeth twice daily with a soft brush and fluoride toothpaste.
Use dental floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria between the teeth.
Deep teeth cleaning (tooth scaling and root planing):
Perform a deep dental cleaning by a dentist to remove tartar and plaque from under the gum line.
Root planing smoothes the surface of the tooth roots, which helps the gums adhere better to the teeth.
Topical or oral antibiotics:
Using antibiotics to eliminate bacteria that cause gingivitis and recession.
Surgical treatments
Gum surgery (gum lift):
Surgery is performed to remove tartar and bacteria from the deep pockets under the gums and stabilize the gums in their natural place.
Gingival vaccination:
Transferring tissue from the roof of the mouth or from other areas of the gums and grafting it into the damaged areas to cover the exposed tooth roots.
Orthopedic surgery:
Surgery to soften and reshape damaged bone that supports the teeth and gums, helping reduce deep pockets and promoting gum healing.
Putting the gums back in place:
Reattaching receding gums to their natural place using advanced surgical techniques.
Modifications in oral care
Changing teeth cleaning techniques:
Use a soft toothbrush and avoid harsh brushing to reduce gum irritation.
Learn correct teeth brushing techniques to maintain healthy gums and teeth.
stop smoking:
Quit smoking to improve gum health and reduce the risk of receding gums.
Teeth grinding treatment:
Use a night guard if a person suffers from grinding teeth during sleep.
Continuing care
Regular visits to the dentist:
Regular follow-up with the dentist for early detection of any gum problems and proper care of them.
In conclusion, gum recession is a common health problem that requires special attention and care to maintain oral and dental health, as by identifying the causes and symptoms of this condition, the necessary steps can be taken to prevent and treat it effectively and good oral care and regular visits to the dentist play a vital role in preventing and treating receding gums and remember, maintaining healthy gums is not just about a beautiful smile, it is an essential part of overall health and well-being and therefore, do not hesitate to consult your dentist as soon as you notice any signs of receding gums, to ensure early intervention and appropriate treatment and with daily attention and a good oral care routine, you can keep your gums and teeth healthy for life.
Read also:






